Let’s play STEM
- 11-14
- Secondary
- 5 hours

Area of Science:
Grade level:
Age of students:
Total time:
Preparation time:
Teaching time:
Teahing methodology to be used:
Gamification- based teaching
Key concepts:
STEM, Gamification
Overview
Introduction to the lesson – Games can play a vital role in keeping students’ motivation for studying Science, as they are learning by playing and playing while learning. In addition, during this scenario, students will not be only games users, but games creators, creating games for their colleagues with topics connected basic concepts in Physics and Science.
Student mission
You need to show your colleagues that SCIENCE is interesting and can be topics of engaging games. Your mission is to create online games to involve your colleagues in studying STEM subjects. You will work in teams and you will be also involved in testing your colleagues’ games.
21st century technical skills gained through this activity
Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics (STEM);
Problem-Solving;
the Four 4Cs: Critical Thinking, Communication, Collaboration, & Creativity.
Related job roles
Careers related information:
Game developer, Content developer, Teacher
Differentiation strategies to meet diverse learning needs
At the beginning of the scenario – preparation time – all students will play the proposed games to test their STEM knowledge, so there will be no differentiation.
During the actual teaching time the differentiation will be evident, as students choose to design their own online game, using their own different skills and creativity. They also need to find their own role in the team, using negotiation skills, also needed for their future career.
This is not a teacher-led activity, but teacher can observe students’ interaction in teams and help them when needed.
Lesson plan
Time for this learning scenario can vary from 4 to 5 hours, depending on the complexity of games created and the time needed to test them in class. Part of the team activities can be carried out from home, mostly online.
Time to complete Lesson
After the lesson:
–Students will learn STEM by playing Kahoot and/or Genial.ly;
-Students will have an opportunity to see real-world application;
-Students will get real-time feedback;
-Students will be motivate by competition.
Expected Learning Outcomes
This lesson is aimed firstly to review students’ knowledge connected with basic concepts in STEM subjects and STEM careers. For the online games or Escape rooms they can use web 2.0 tools like KAHOOT! or Genial.ly .
Prior knowledge and vocabulary
Science and Engineering/Math Practices
Pupils combine goals of research, design and realization. They test their games in class and make proposals to improve the design or the game’s rules. In this way, they develop insight into design methods and realization techniques and their interactions.
STEM knowledge, STEM language, STEM careers info are also revised and improved during the learning scenario.
Curriculum Alignment
Engage: Teacher helps students reflect on what they already know and identify any knowledge gaps. It is important to foster an interest in the upcoming concepts so students will be ready to learn. Teachers might task students with asking opening questions or writing down what they already know about the topic. This is also when the concept is introduced to students for the first time.
Materials: computer, projector, internet connection
Preparation: 3 Minutes
Facilitation of Learning Experience: 5 Minutes
Transition: 2 Minutes
Teacher will: present the topic of educational games and their importance in learning any subject, including STEM. Class discussion started.
Students will: Participate in the discussion and give examples of games with STEM topics they have used till now.
Explore: During the exploration phase, students actively explore the new concept through concrete learning experiences. They might be asked to go through the scientific method and communicate with their peers to make observations. This phase allows students to learn in a hands-on way.
Materials: computer, internet connection, whiteboard, markers
Online games:
https://create.kahoot.it/share/wish-women-in-stem-here-now/8a9f6daa-db5b-4082-90af-09aa7b3393cb
https://view.genial.ly/60c8469888a39e0dc86f884d
Offline games:
– Crosswords – students go one by one to the blackboard, writing words related to Science, vertically and horizontal, only with the letters of the previous word. Students get eliminated from the game if:
– repeat an already written word;
– can’t find the connection with Science or give a wrong explanation;
– can’t find a proper Science word in 1 minute.
– Three minutes of STEM: after a student says the alphabet in his mind and we choose a letter, all students have 3 minutes to write as many STEM notions starting with that letter. The student who has discovered the biggest amount of words will read them. Each word will be explained and its connection with STEM justified. The same student then says the alphabet and chooses the next letter.
– Vertical words: one student proposes a word related to STEM, it is written vertically on the board, and the others will write on the notebooks words starting with all the letters, of course related to STEM. The first one to finish shouts STOP, receives the right to write on the board and complete the chosen words and then proposes a new vertical word.
Preparation: 2 Minutes
Facilitation of Learning Experience: 35 Minutes
Transition: 3 Minutes
Teacher will: Introduce some examples of offline and online STEM related games. Choose one or more games and challenge students to play.
Students will: Play the games and observe their design and rules. They review their STEM knowledge by playing.
Explain: This is a teacher-led phase that helps students synthesise new knowledge and ask questions if they need further clarification. For the Explain phase to be effective, teachers should ask students to share what they learned during the Explore phase before introducing technical information in a more direct manner, according to “The 5E Instructional Model: A Learning Cycle Approach for Inquiry-Based Science Teaching.” This is also when teachers utilise video, computer software, or other aides to boost understanding.
Materials: computers, internet connection, stationary
Preparation: 5 Minutes
Facilitation of Learning Experience: 5 Minutes
Transition: 5 Minutes
Teacher will:
Organize students in teams, using an online tool like https://www.classtools.net/random-name-picker/ or asking them to organize teams based on common interests.
Explain the characteristics of a good educational game (See Annex III). Challenge teams to create STEM related online games that will be tested by the whole class.
Students will: take roles in teams and start negotiating for choosing the type of game to create.
Students will learn more about the two web tools they will use,
- KAHOOT!
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zBkVp8-CDeo
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1OqZ7ApaTgU
- ly
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fELfErCCiPk
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x-LNas33tc4
Elaborate: The elaboration phase of the 5E Model focuses on giving students space to apply what they’ve learned. This helps them to develop a deeper understanding. Teachers may ask students to create presentations or conduct additional investigations to reinforce new skills. This phase allows students to cement their knowledge before evaluation.
Materials: computers, internet connection,
Preparation: 3 Minutes
Facilitation of Learning Experience: 90 Minutes
Transition: 2 Minutes
Teacher will: Facilitate team work and help teams/students in difficulty
Students will: Decide together and start creating their own STEM game, meaning:
- Type and name of the game;
- Materials and tools needed;
- Rules and goals;
- Rewarding system;
- Questions/challenges database.
This phase can be also continued at home, as a collaborative task for the whole team. They prepare the final product- a STEM game.
Evaluate: The 5E Model allows for both formal and informal assessment. During this phase, teachers can observe their students and see whether they have a complete grasp of the core concepts. It is also helpful to note whether students approach problems in a different way based on what they learned. Other helpful elements of the Evaluate phase include self-assessment, peer-assessment, writing assignments, and exams.
Materials: computer, internet connection, stationary
Preparation: 5 Minutes
Facilitation of Learning Experience: 100 Minutes or more
Transition: 5 Minutes
Teacher will: Observe and assess teams’ developed games using a suitable rubrics
Students will:
Introduce their developed games to the whole class, play their colleagues games and give feedback. Refresh their STEM knowledge during game playing.
Independent learning tasks (ILT): Provide two-three challenges to students to complete before the next lesson.
*Improve your STEM game using colleagues’ suggestions.
*Launch the improved games as challenges in your online classes.
Lesson
Strategies for student feedback within the lesson
Feedback will be given immediately after playing the games, in terms of quality of the designed games – informal feedback.
Student feedback
Alignment of achieved skills and knowledge across other subjects and also teachers may wish to expand on the lesson in various ways.
Online games: IT
Formulas with score: Mathematics
Game design: Art
Storytelling: Language
Curriculum mapping of outcomes attained
Describe the type(s) of assessment that is suitable for the lesson.
After playing the game, the teams assess each other’s work. (peer-assessment)- informal assessment
Also, the teacher will assess not only the quality of the games presented, but also the team work and collaboration using a rubric (teacher assessment) – formal assessment.
Materials
Materials used for the lesson and online resources
computer, projector, internet connection, whiteboard, stationary
* https://create.kahoot.it/share/wish-women-in-stem-here-now/8a9f6daa-db5b-4082-90af-09aa7b3393cb
* https://view.genial.ly/60c8469888a39e0dc86f884d
* https://www.classtools.net/random-name-picker/
* https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zBkVp8-CDeo
* https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1OqZ7ApaTgU
Preparation
Description of what activities should be prepared before the lesson
A folder will be created containing everything the learning scenario needs.
Team Work
Description of the 21st century skills gained linked to job roles.
Students will work in teams to create the educational online games. They will need negotiation skills, digital skills, collaboration skills, all of them required for future jobs.
Rubrics
Include a scoring guide to evaluate the quality of students’ assessment responses. As students will test their colleagues games, we will use also a peer-to-peer assessment Rubric ( See Annex II)
| Scale of Independent Work | ||||||||
| Zero
Independence |
A lot of Help
with Some Independence |
Semi
Independent |
Fully
Independent |
|||||
| Teacher gives students a full method with
clear instructions for how to develop the game. |
Teacher gives students an
outline for the procedure but allows options at different steps. |
Teacher
specifies the example. Students research the method to develop the game. |
Students choose real time
example and try to solve all problems during the game development. |
|||||
| Observation and Assessment of Competencies | ||||||||
| Follow written and oral
procedures |
Students follow written and oral instructions | Students follow written and oral instructions,
making individual choices |
Students follow a method they have researched | Students follow a method they have researched | ||||
| Safely uses a
computer and materials |
Students follow instructions on how to safely
use the computer. |
Students follow instructions on the safe use the computer. | Students
minimise risks with minimal prompting. |
Students carry out a full risk
assessment and minimise risks. |
||||
| Makes records and results
observations |
Students record results data in specified ways. | Students record results data in specified ways. | Students record precise and
accurate data, methodically using the specified ways. |
Students choose the most
effective way of recording precise and accurate data. |
||||
Ek
Annex I
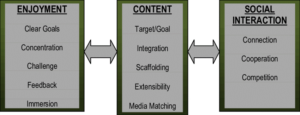
Annex II
PEER ASSESSMENT RUBRIC
Your peers will play your game and then assess the game based on the criteria below.
Name of game: _________________________________________
Who created the game: __________________________________
Who played the game: ___________________________________
On a scale of 1-4, rate the following 4 categories for the game you played.
1 = Not al all 2 = somewhat 3 = For the most part 4 = YES!
| Category | Criteria | Score |
| Rules | Were the rules clearly outlined and easy to understand? | |
| Accuracy | Was the information accurate and complete? | |
| Effort | Was there effort put into creating this game? | |
| FUN! | Did you have full playing this game? | |
| AVERAGE SCORE
(add up the 4 scores and divide by 4) |
||

