Smart Sensor Game
- Technology
- 14-16 years
- Secondary school level (14-18 years old)
- 2 hours
Area of Science:
Grade level:
Age of students:
Total time:
Preparation time:
Teaching time:
Teahing methodology to be used:
Game-based lesson
Key concepts:
By examining certain smart sensor applications, students discover the differences between smart sensors and standard sensors.
Students play a card game to help them remember what they’ve learned about electronic systems.
Overview
Smart sensors are playing an increasingly important part in our daily lives. The Smart Sensor Communications topic delves into what smart sensors are, how they are utilized now, and how they might be used in the future.
Students learn about some of the most current advancements in the use of smart sensors in control systems. Many of these applications are in health-care and other high-tech fields.
By examining certain smart sensor applications, students discover the differences between smart sensors and standard sensors.
Students play a card game to help them remember what they’ve learned about electronic systems.
Presentation and explanation of a complete system to other students once it has been collected.
Student mission
The aim of the game is to make as many systems as possible, i.e. an Input with a Process and an Output, and state what the system is going to do.
To facilitate the game, the students can decide what the ‘process cards’ will do with the input signal. Players: 3 to 6 players per group.
- Each player is dealt 4 cards, which they keep hidden from other players.
- Place the remainder of the pack face-down in the centre and turn the top card over and place it beside the face-down pack.
- Randomly choose a player to go first.
- The first player can choose to take the card that has been turned over OR one from the top of the centre pack.
- Once a card has been chosen, this player must then return a card from their hand face-up next to the centre pack.
- The next player can choose to take a card from the top of the centre pack OR one from the discarded pile.
- They then return a card face-up to the pile beside the centre pack.
- This continues, with all players taking their turn.
- When a player collects a set of cards that complete a system (i.e. Input/Process/Output), they must immediately show the set to the other players and place the three cards face-down in front of themselves.
- When the centre pack has no cards remaining, the discarded pile is inverted and a card turned over.
- The game continues until a player has no cards left, or the pack has been exhausted, or a time limit has expired.
- The winner is the player with the most completed systems.
Tie-breaker
- In a case of a tie (this could happen in a timed game) the player with the least number of cards in their hand is the winner.
21st century technical skills gained through this activity
List of skills:
- Science
- Design
- Technology
- Technological literacy
- Competition
- Critical thinking
- Communication
- Game-based learning
Related job roles
Game designer
Graphic designer for games
Programmer
Website developer
Differentiation strategies to meet diverse learning needs
Gamification, Classroom response systems, Forming and framing questions, Students are encouraged to work collaboratively with their peers.
Lesson plan
2 hours approximately
Time to complete Lesson
Know about the difference between simple sensors and smart sensors
Know about some applications of smart sensors
Know that all technological developments have advantages and disadvantages
Students must present and explain a complete system to their fellow students once it has been collected.
Expected Learning Outcomes
Inputs
Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
Thermistor
Moisture Sensor
Process
Single transistor
Darlington Pair
Output
Motors
Bulbs
LED
Buzzer
Prior knowledge and vocabulary
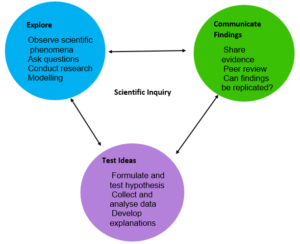
Use the Scientific Inquiry model and the Test Your Idea template to help you with your investigative question. See Annex I. and II.
Science and Engineering/Math Practices
It can be used on the development of technology games, web design, how automatic doors work etc.
Curriculum Alignment
Engage: Teacher helps students reflect on what they already know and identify any knowledge gaps. It is important to foster an interest in the upcoming concepts so students will be ready to learn. Teachers might task students with asking opening questions or writing down what they already know about the topic. This is also when the concept is introduced to students for the first time.
The teacher will introduce the topic by using a mobile phone with a proximity sensor to demonstrate how the screen of the phone turns off once it is brought near the ear. This will attract the students’ interest and can spark a discussion on sensors. This way the teacher can check students’ prior knowledge and introduce new ideas.
Materials: mobile phone with a proximity sensor
Preparation: [2] Minutes
Facilitation of Learning Experience: [5] Minutes
Transition: [2] Minutes
Teacher will: introduce the topic, facilitate discussion, lead and answer Q&A
Students will: listen intently, bring schemata to mind
Explore: During the exploration phase, students actively explore the new concept through concrete learning experiences. They might be asked to go through the scientific method and communicate with their peers to make observations. This phase allows students to learn in a hands-on way.
Teacher uses the Smart Sensors presentation to explain and introduce smart sensors, as well as to answer some basic questions about their nature and applications.
Work through the smart sensors presentation as a whole class activity. Produce a word list to help, for example:
- Adaptive – able to change their output
- Transducer – device that detects an energy transfer
- Proximity — closeness to
- Amplify — make bigger
- Multi-sensing – using more than one input to make a decision
- Constraint — difficulty.
Materials: projector and screen, smart sensors presentation (see Annex III for the presentation)
Preparation: [5] Minutes
Facilitation of Learning Experience: [20] Minutes
Transition: [5] Minutes
Teacher will: lead the presentation, lead the Q&A session at the end of the presentation
Students will: take notes of the presentation
Explain: This is a teacher-led phase that helps students synthesise new knowledge and ask questions if they need further clarification. For the Explain phase to be effective, teachers should ask students to share what they learned during the Explore phase before introducing technical information in a more direct manner, according to “The 5E Instructional Model: A Learning Cycle Approach for Inquiry-Based Science Teaching.” This is also when teachers utilise video, computer software, or other aides to boost understanding.
Materials: smart sensor communications
Preparation: [5] Minutes
Facilitation of Learning Experience: [20] Minutes
Transition: [0] Minutes
Teacher will:
Students will:
Elaborate: The elaboration phase of the 5E Model focuses on giving students space to apply what they’ve learned. This helps them to develop a deeper understanding. Teachers may ask students to create presentations or conduct additional investigations to reinforce new skills. This phase allows students to cement their knowledge before evaluation.
Materials: Smart sensor Card game
Preparation: [5] Minutes
Facilitation of Learning Experience: [35] Minutes
Transition: [2] Minutes
Teacher will: support the process
Students will: play the card game and learn
Evaluate: The 5E Model allows for both formal and informal assessment. During this phase, teachers can observe their students and see whether they have a complete grasp of the core concepts. It is also helpful to note whether students approach problems in a different way based on what they learned. Other helpful elements of the Evaluate phase include self-assessment, peer-assessment, writing assignments, and exams.
Materials:
Preparation: [ ] Minutes
Facilitation of Learning Experience: [ ] Minutes
Transition: [ ] Minutes
Teacher will:
Students will:
Independent learning tasks (ILT): Provide two-three challenges to students to complete before the next lesson.
- Students will research real life applications of what they have learned within the classroom
- Students will answer post class questions
Students will work in groups to prepare presentations and to present them to their class
Lesson
Students will receive feedback on their performance in both the questionnaire and the course in general. Students will also give feedback on whether they liked the way the lesson was conducted and the content.
Student feedback
The knowledge gained by the students in all 4 subjects can also be useful in the field of Physics and Mathematics.
Language use if English is not the main language.
Students have to do research themselves in order to explain their system to the fellow students, they learn to use presentation software and a computer.
Curriculum mapping of outcomes attained
Practical, student presentation, time bound assessment and Q&A.
After finishing their game, students present their game by giving a presentation.
They can also create a game design or sprites at home in preparation for a lesson.
Materials
Deck
52-card deck per group. (see Annex2)
Students will use the card template provided to create a deck of cards for each group.
Each deck should consist of:
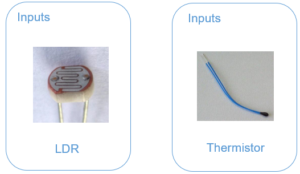
15 INPUTS:
Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) x 5
Thermistor x 5
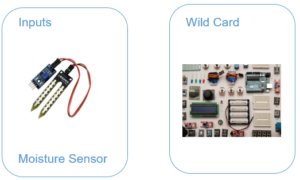
Moisture Sensor x 5
20 PROCESS:
Single transistor x 10
Darlington Pair x 10
16 OUTPUT:
Motors x 4
Bulbs x 4
LED x 4
Buzzer x 4
1 WILD CARD:
Students can decide what it should be
Preparation
Teacher will create a folder which contains everything students will need before the game.
This folder contains:
- Images that can be used in the game
- Example of the game
- Instructions
Team Work
Students will work together in groups of 3-6 persons. This will help t to create a sense of teamwork and solidarity between them. They will learn to listen and help their colleagues. It also creates a sense of competition, which can improve team efficiency.
Rubrics
|
|
Zero
Independence |
A lot of Help
with Some Independence |
Semi
Independent |
Fully
Independent |
| Teacher gives
students full method with clear instructions for how to carry out the game. |
Teacher gives
students an outline for the procedure but allows options at different steps. |
Teacher
specifies the example. Students research the method to develop the game. |
Students choose real time
example and try to solve all problems by developing programs |
|
| Follow written and oral
Procedures
|
Students follow written and oral instructions
|
Students follow written and oral instructions,
making individual choices in developing game. |
Students follow a method they have researched
|
Students follow a method they have researched
|
| Safely uses a
computer and materials |
Students follow instructions on how to safely
use the computer. |
Students follow instructions on the safe use the computer. | Students
minimize risks with minimal prompting. |
Students carry out a full risk
assessment and minimise risks. |
| Makes records and results
observations |
Students record results data in specified ways.
|
Students record results data in specified ways. | Students record precise and
accurate data, methodically using appropriate example.
|
Students choose the most
effective way of recording precise and accurate data methodically using appropriate example |
| Research,
references and reports
|
Data is reported and conclusions drawn. Students carry out
presentations on the development of games with a lot of guidance. |
Data is reported and conclusions drawn. Students compare results and identify
reasons for differences. Students carry out presentations on the development of games with some guidance. |
Students
research methods available. They compare results and report on differences. Appropriate software is used to process data and report findings. Students carry out presentations on the development of games with minimal prompting.
|
Students
research alternatives in order to plan their work. Reporting covers the planning, carrying out and an analysis of their results. Appropriate software and/or tools are used to process data and report findings. Students carry out presentations on the development of games without the help of the teacher.
|
| Analyses
problems and identifies requirements: Identifies correct input/ output |
Students are
unable to identify any input and output. |
Students are
able to identify only one input or output. |
Students are
able to identify correctly some input and output. |
Students are
able to identify correctly all input and output and provide alternatives. |
| Demonstrates program in
front of the class
|
Students are
unable to explain program design |
Students are
able to explain a little program design. |
Students are
able to explain the entire program design correctly as it is. |
Students are
able to explain the program design correctly and provide alternative solutions. |
Ek
Annex. I.
Scientific Inquiry
Annex II.
Sensor Card Game Templates
Annex III.
Smart sensors presentation can be found here: https://drive.google.com/drive/u/0/folders/1RIeN6j12jrGTWfxIyCP0UItwUw4TSuwr

